The “Culprits” Behind PVC Screw Breakage and Countermeasures
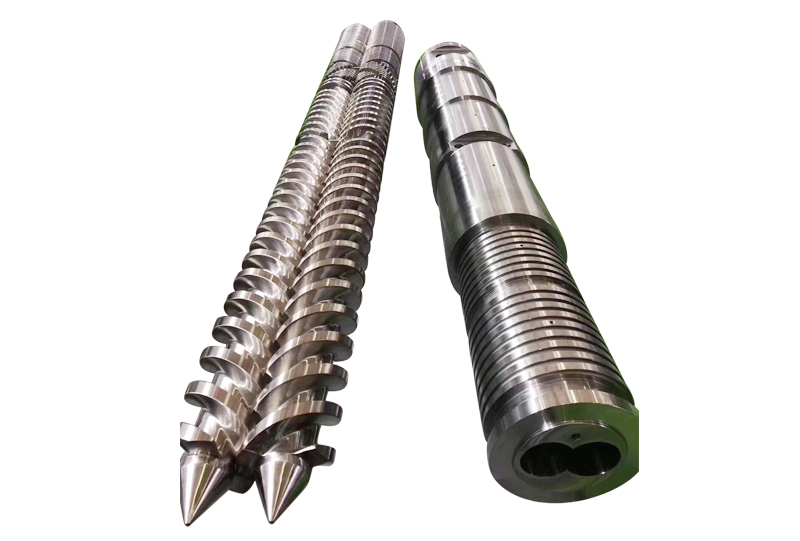
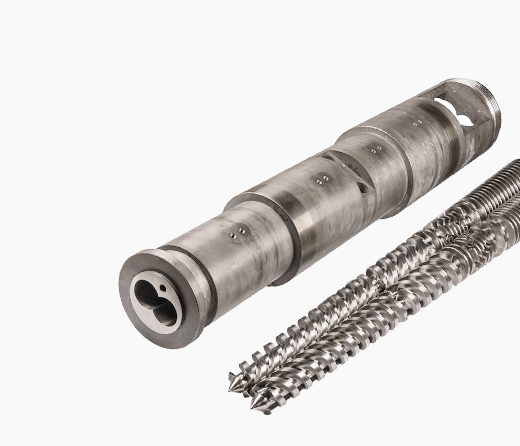
In the PVC extrusion industry, screw breakage is a common issue that severely impacts production efficiency and product quality. Screw breakage is typically categorized into normal wear breakage and abnormal breakage. Below is an analysis of the causes of these two types of breakage and preventive measures: 1.Screw Processing and Materials **Material Selection** – Barrel Material: Commonly used materials include Cr12MoV (SKD61 alloy steel) and 38CrMoAlA. – Screw Material: 38CrMoAlA is typically chosen. **Heat Treatment Process** – Barrel: Tempering is used to homogenize the internal structure and improve the metallurgical grade. Two-stage alloy steel parts undergo overall quenching, achieving a hardness of HRC60 after quenching. – Screw: The final heat treatment is surface nitriding, with a nitriding depth of 0.5-0.7 mm. Large companies can achieve a nitriding depth of over 0.6 mm. **Bimetal Processing Methods** Metal processing methods generally include forging (for large parts) and casting (for small parts). **Service Life** The service life of the screw is related to the filler content: – For ≤100 parts calcium: 1-2 years – For 100-200 parts calcium: ~1 year – For 200-300 parts calcium: 6-8 months – For >300 parts calcium: 3 months 2.Influence of Screw Structural Characteristics on Pipe Processing and Mechanical Properties **Requirements for Screw Structure Based on Filler Content** – >120 parts: Smaller metering section gap, increased mixing grooves, and high-calcium screws. – <80 parts: High-calcium screws with reduced feed and metering section flight gaps. – <30 parts: Feed mixing section and compression section combined, with larger metering section